Islam, the world’s second-largest religion, is founded on a set of core practices known as the Five Pillars. These fundamental acts of worship form the backbone of a Muslim’s spiritual journey, providing a roadmap to connect with Allah and lead a life of devotion. In this article, we will dive into each of the Five Pillars of Islam, exploring their significance through the lens of the Quran and Hadith. We aim to explain these essential concepts in simple and accessible language, making them understandable for all.
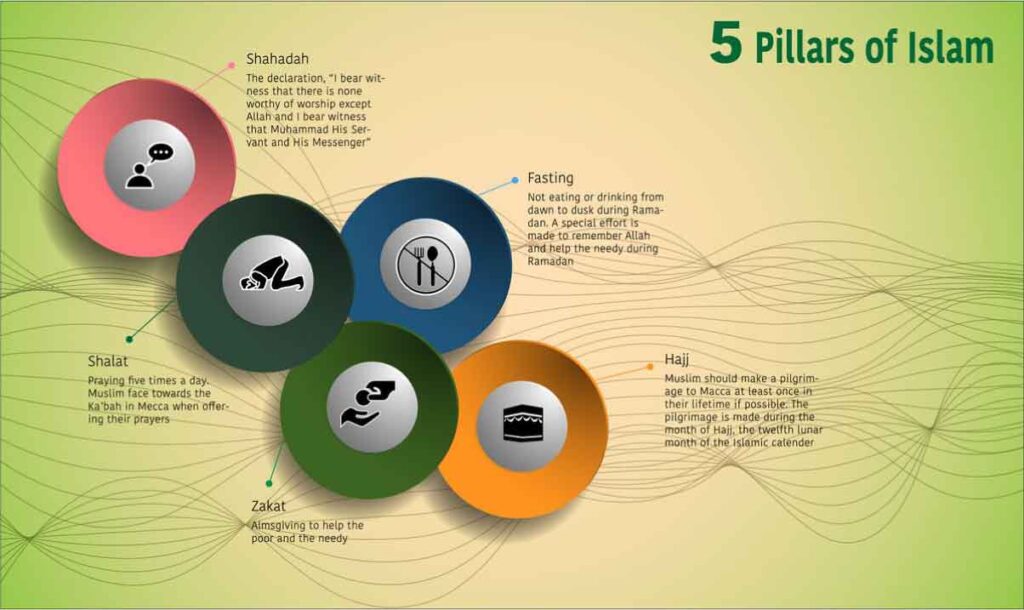
Five Pillars of Islam
1. Shahada (Declaration of Faith)
The Shahada, the first pillar of Islam, underscores the central monotheistic belief that there is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is His messenger. This profession of faith is at the heart of Islamic theology, affirming the unity of Allah and the guidance brought by the Prophet Muhammad. This declaration is recited daily by Muslims and holds profound significance, encapsulating the essence of their faith.

Quranic Basis:
“Say, ‘He is Allah, [who is] One, Allah, the Eternal Refuge. He neither begets nor is born, nor is there to Him any equivalent.'”
(Quran, Surah Al-Ikhlas, 112:1-4)
Hadith:
The Prophet Muhammad stated: “Whoever testifies that there is no god but Allah, alone, without partner, and that Muhammad is His servant and His Messenger, and that Jesus is His servant and His Messenger, and His Word which He cast into Mary and a Spirit from Him, and that Paradise is true, and that the Hellfire is true, Allah will admit him into Paradise with whatever deeds he accomplished.”
(Sahih al-Bukhari)
2. Salah (Prayer)
Salah, or prayer, is the second pillar of Islam and serves as a direct connection between a Muslim and Allah. Muslims perform five daily prayers, facing the Kaaba in Mecca, as a testament to their submission to the Divine. Prayer is a source of solace and guidance, allowing believers to pause amidst their daily activities and seek Allah’s presence.
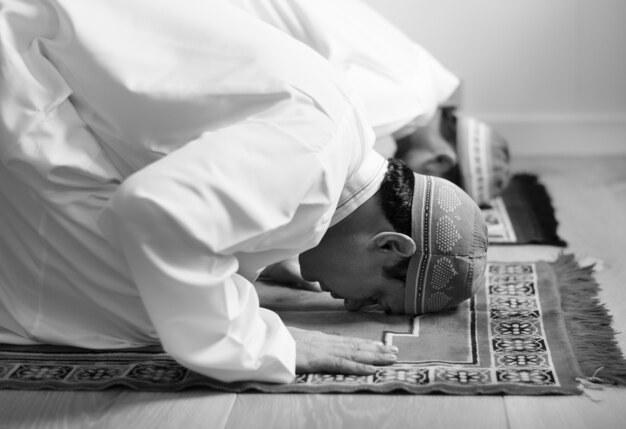

Quranic Basis:
“Establish prayer and give zakah and bow with those who bow [in worship and obedience].”
(Quran, Surah Al-Baqarah, 2:43)
Hadith:
The Prophet Muhammad said: “When a servant stands in prayer, his sins are placed on his head and shoulders. Whenever he bows or prostrates, they fall away from him.”
(Sahih al-Bukhari)
3. Zakat (Almsgiving)
Zakat, the third pillar, emphasizes the importance of sharing one’s wealth with those less fortunate. It promotes social justice and compassion within the Muslim community. Muslims give a portion of their wealth, typically 2.5%, to support the needy, fostering a sense of solidarity and eliminating inequality.
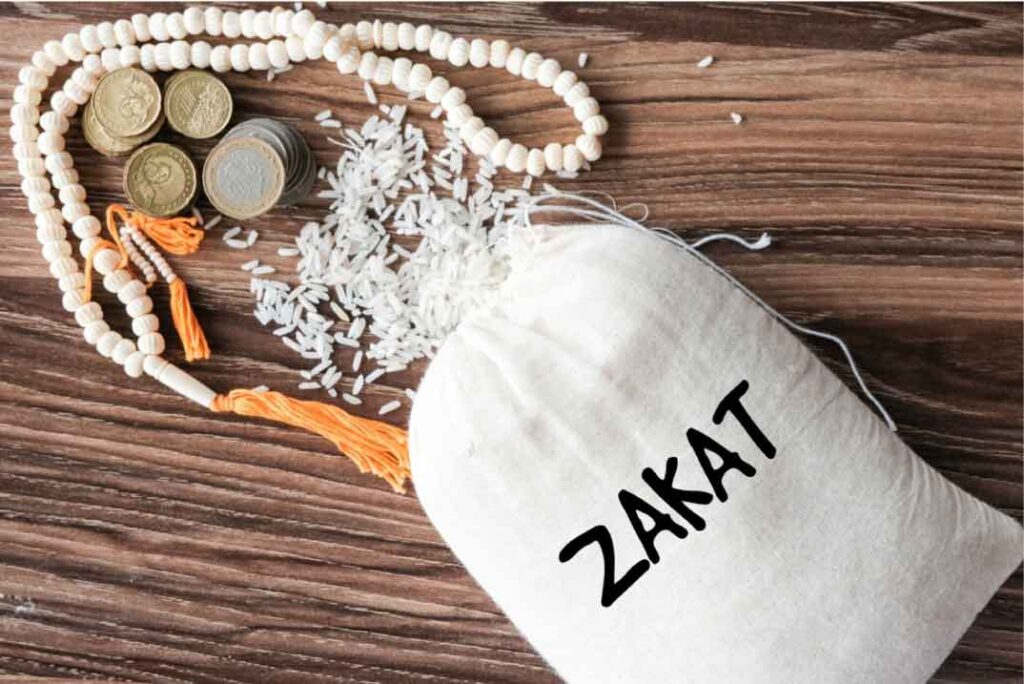

Quranic Basis:
“Take, [O, Muhammad], from their wealth a charity by which you purify them and cause them increase, and invoke [ Allah ‘s blessings] upon them. Indeed, your invocations are reassurance for them. And Allah is Hearing and Knowing.”
(Quran, Surah At-Tawbah, 9:103)
Hadith:
The Prophet Muhammad said: “The believer’s shade on the Day of Resurrection will be his charity.”
(Sunan Ibn Majah)
4. Sawm (Fasting)
Sawm, or fasting, is observed during the holy month of Ramadan. Muslims abstain from food, drink, and other physical needs during daylight hours, focusing on spiritual reflection, self-discipline, and empathy for the less fortunate. Fasting encourages believers to develop self-control and gratitude.

Quranic Basis:
“O you who have believed, decreed upon you is fasting as it was decreed upon those before you that you may become righteous.”
(Quran, Surah Al-Baqarah, 2:183)
Hadith:
The Prophet Muhammad said: “Fasting is a shield, so the one who fasts should avoid obscene speech and ignorant behavior. If someone fights or abuses him, he should reply by saying: ‘I am fasting!'”
(Sahih al-Bukhari)
5. Hajj (Pilgrimage)
Hajj, the final pillar, is the pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca. Muslims who are physically and financially capable undertake this journey at least once in their lifetime. It symbolizes unity, humility, and the culmination of a believer’s devotion to Allah.
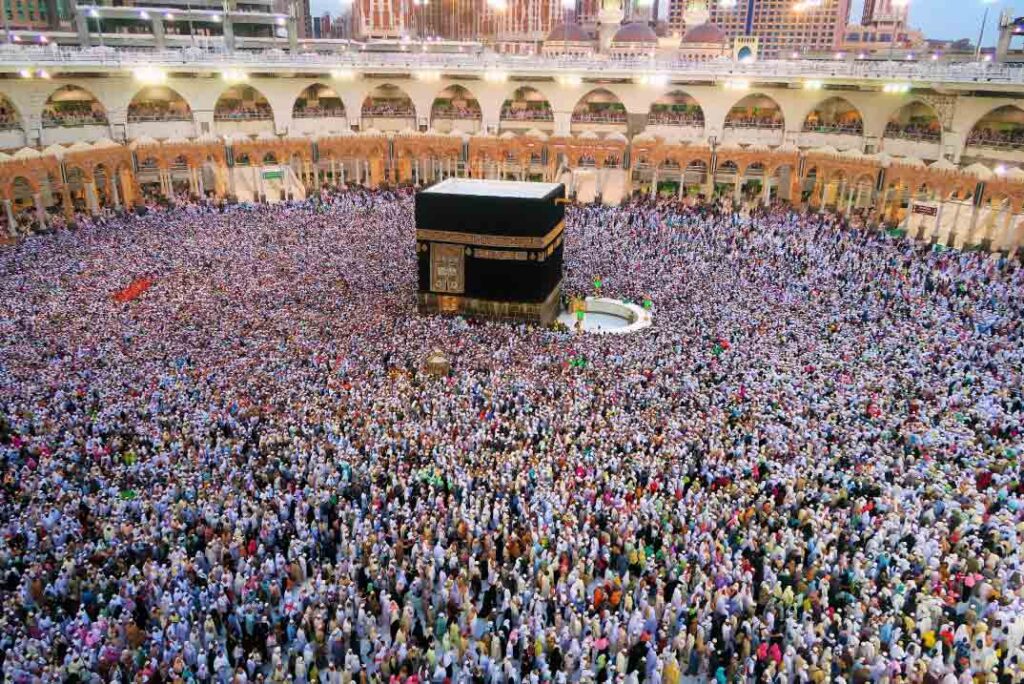

Quranic Basis:
“And [mention] when We made the House a place of return for the people and [a place of] security. And take, [O believers], from the standing place of Abraham a place of prayer. And We charged Abraham and Ishmael, [saying], ‘Purify My House for those who perform Tawaf and those who are staying [there] for worship and those who bow and prostrate [in prayer].'”
(Quran, Surah Al-Baqarah, 2:125)
Hadith:
The Prophet Muhammad said: “Whoever performs Hajj for Allah’s pleasure and does not have sexual relations with his wife and does not do evil or sins, then he will return (after Hajj free from all sins) as if he were born anew.”
(Sahih al-Bukhari)
Conclusion
The Five Pillars of Islam form the cornerstone of a Muslim’s faith and practice. Through these acts of worship, Muslims establish a profound connection with Allah, cultivate compassion for their fellow beings, and seek a life of righteousness. As articulated in the Quran and Hadith, these pillars guide believers on their spiritual journey, helping them navigate life’s challenges with faith, devotion, and a commitment to self-improvement.
May Allah Bless Us All!
What is Tawhid ? The One Powerful God in Islam